Capture wireless packets in monitor mode in Linux
Share on:Edit on:Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Check if your Linux OS supports monitor mode
- Setup new wireless interface in monitor mode
- Use wireshark to capture wifi traffic
- Restore your original wireless interface
Introduction
In this tutorial, I will be showing how to setup a wireless interface in monitor mode and how to capture wireless network traffic using wireshark.
I have been using Kubuntu Linux system to demonstrate this tutorial. This tutorial can be adapted to other Linux based distributions easily.
Check if your Linux OS supports monitor mode
Most, if not all, of the the modern wifi adapters shipping with laptops/desktops support capturing wireless traffic in monitor mode. If you need cheap and best option, you could choose Raspberry Pi 3B+ or Raspberry Pi 4B. Both SBCs support capturing in monitor mode through their Broadcom chipsets.
To check if your Linux kernel driver supports monitor mode, use the following command.
iw list | grep -i "supported interface modes" -A 20 | grep "* monitor"
If you don’t get any output, either your wifi chipset or the wifi driver doesn’t support monitoring wifi. Mostly it would be latter case. Note that for Raspberry Pi devices, you might need to install Kali Linux. It’s an Ubuntu based system customized for most networking related tasks.
Setup new wireless interface in monitor mode
Even though, it’s possible to use the existing wireless interface (in my case it is wlp2s0), the Ubuntu system reverting the interface back from monitor mode to managed mode. So I thought of deleting it and creating a new interface for monitoring purpose. You could restore your original wireless interface back using the commands mention here. Please note down your wifi interface name using ip link command. It looks like wlp2s0 or wlan0.
Create new wireless interface in monitor mode
Lets create a new interface called mon0, delete the existing interface and finally bring up the new interface up. Don’t forget to replace the interface name wlp2s0 with yours.
# Create new interface called mon0
sudo iw phy phy0 interface add mon0 type monitor
sudo iw dev wlp2s0 del # Replace wlp2s0 with your interface name
sudo ip link set mon0 up # Bring up the interface mon0 up
You can check if your wireless interface mon0 is created successfully in monitor mode or not, using the following command.
iw dev
The output would be similar to following
phy#0
Interface mon0
ifindex 6
wdev 0xa
addr ad:ec:1c:aa:d3:c7
type monitor
You could see one of the line as type monitor.
Set the channel frequency for the mon0
Obviously you are going to capture wireless traffic for certain channel. For ex: channel 44, 60, 112 etc. We need to set the respective channel frequency to be captured by mon0. You can find the frequency of certain channel from following table.
| Channel | Frequency |
|---|---|
| 1 | 2412 |
| 6 | 2437 |
| 11 | 2462 |
| 36 | 5180 |
| 40 | 5200 |
| 44 | 5220 |
| 48 | 5240 |
| 52 | 5260 |
| 56 | 5280 |
| 60 | 5300 |
| 64 | 5320 |
| 100 | 5500 |
| 104 | 5520 |
| 108 | 5540 |
| 112 | 5560 |
| 116 | 5580 |
| 120 | 5600 |
| 124 | 5620 |
| 128 | 5640 |
| 132 | 5660 |
| 136 | 5680 |
| 140 | 5700 |
| 144 | 5720 |
| 149 | 5745 |
Now, set the channel frequency using the following command
sudo iw dev mon0 set freq <Channel Freq>
For example if I want to capture wirless traffic on channel 44, from the above table, the channel frequency is 5220. So the command would be
sudo iw dev mon0 set freq 5220
Use wireshark to capture wifi traffic
Wireshark is a packet analyzer. We can select the specific interface, in this case mon0, and then start capturing. Run the following command in terminal to install wireshark.
sudo apt install wireshark
When it prompts to select the installation for non-root users, select yes. You might need to run the following commands to make wireshark run properly.
sudo usermod -a -G wireshark $USER
sudo adduser $USER wireshark
Launch the wireshark form Application Launcher. It should show all the interfaces available in the system as shown in the below figure. If the interfaces are not showing up, then logout and logging into the system might be needed to take effect the above wireshark configuration. In that case, you might need to follow the tutorial from the start.
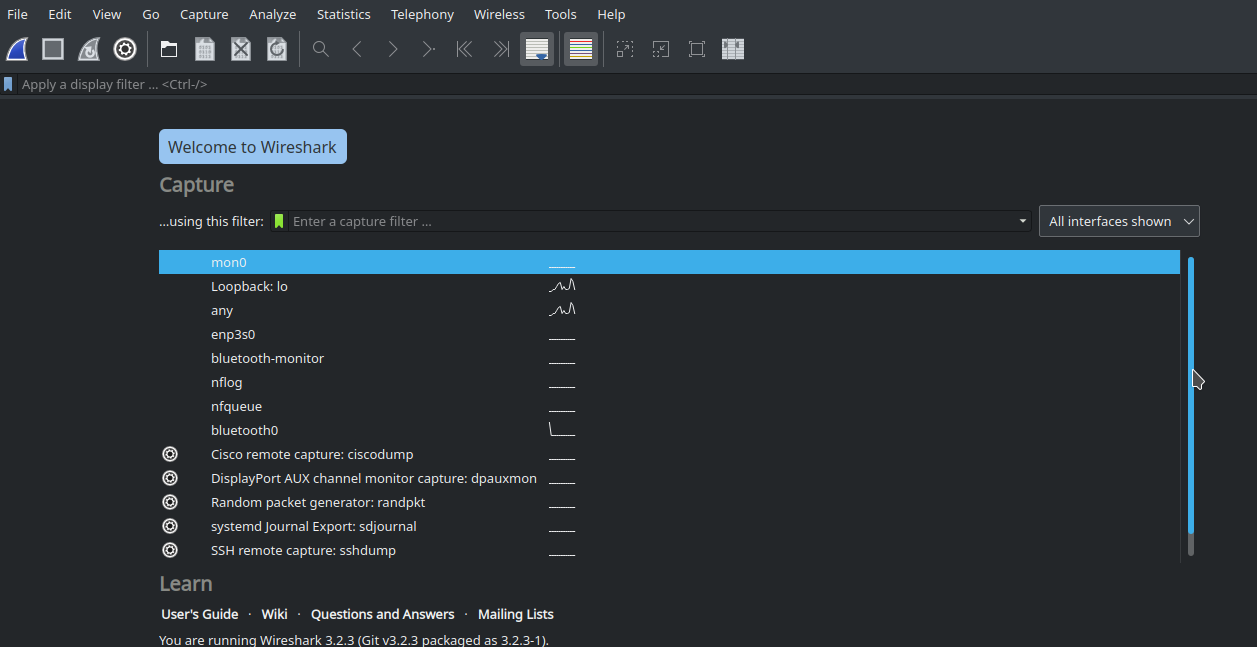
Select the interface to be captured (mon0) and start capturing the wireless traffic by clicking the blue button. Once you done with the capture, click on red button to stop the capture. Go to File -> Save as menu to save the capture.
Restore your original wireless interface
To restore your original interface and to delete the mon0 interface, run the following commands. Replace wlp2s0 with your original wifi interface noted at the starting of the tutorial.
sudo iw dev mon0 del
sudo iw phy phy0 interface add wlp2s0 type managed